Subfamily MYRMICINAE
GENUS
Monomorium
Mayr, 1855
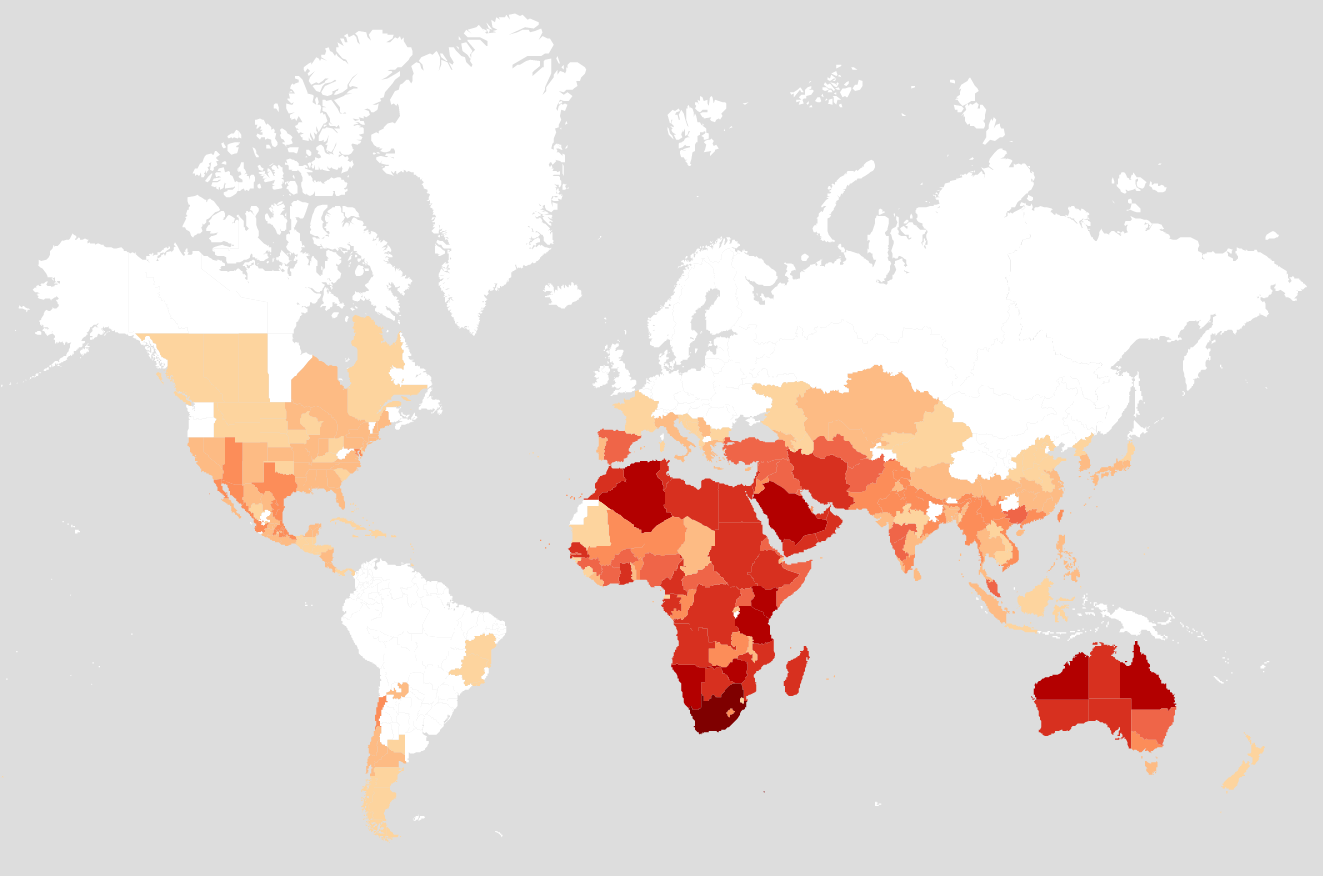
Distribution.
A large ant genus with 296 species described. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, with the exception of northern parts of the northern hemisphere and Central South America. There are several well-known household pest ant species with global distribution from this genus.
Biology & Ecology.
Nests of Monomorium species are usually located within the soil or decaying wood. Nests are large, contain tens of thousands of workers to more than a million of workers, forming polygynous colonies (more than one egg-laying queen per colony).
Monomorium species are general scavengers that usually forage above the ground. Some species are known for having ergatoid (wingless) queens.
Identification.
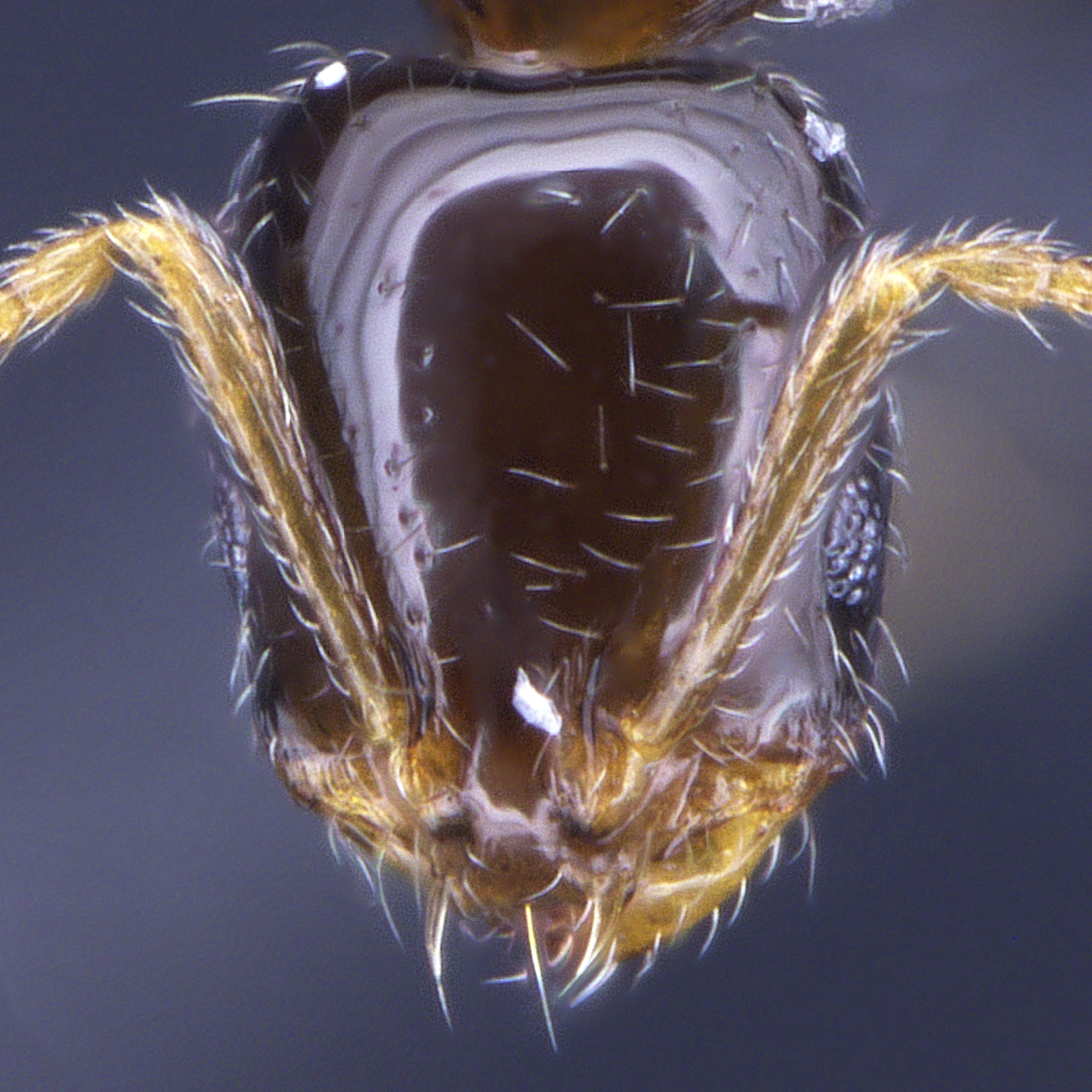
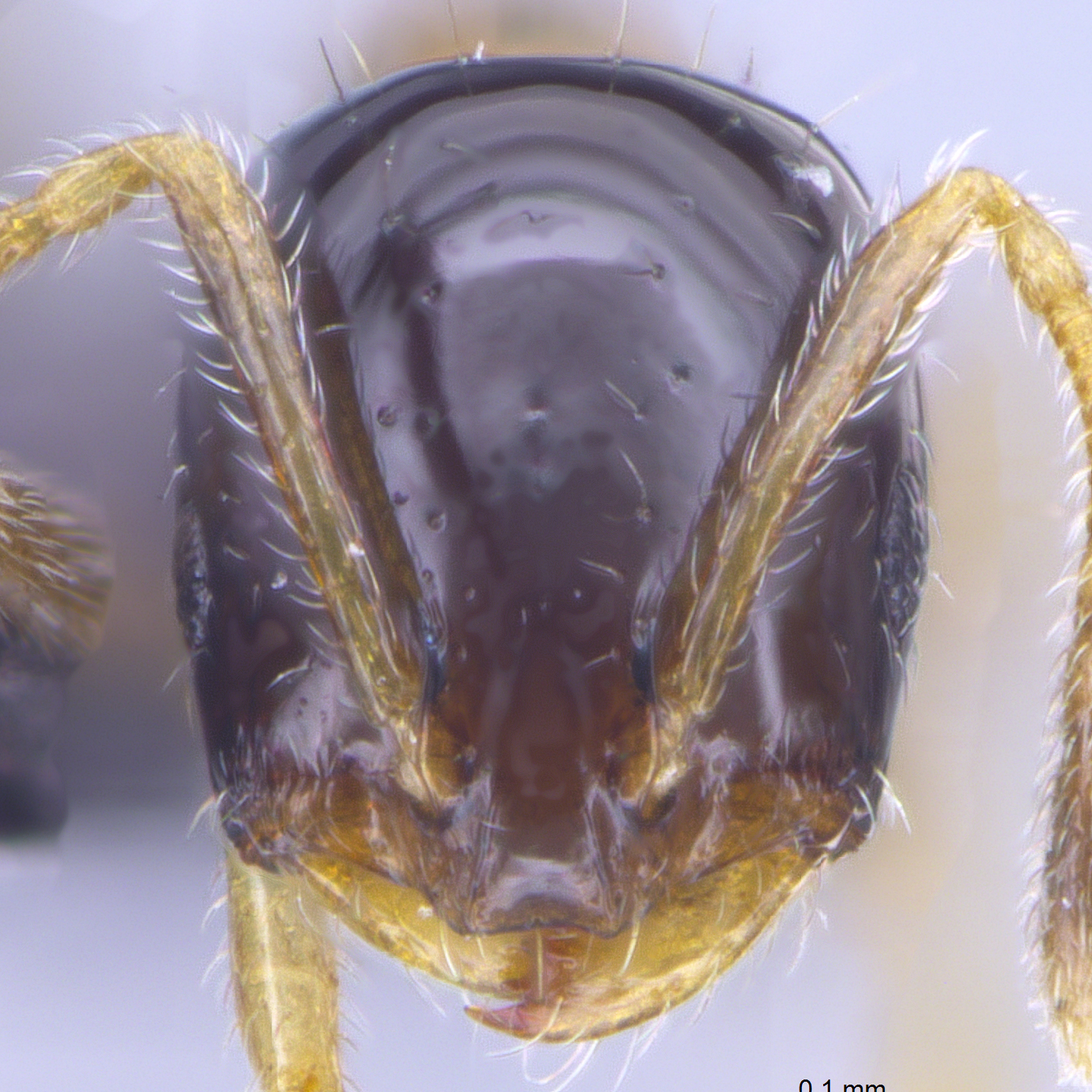
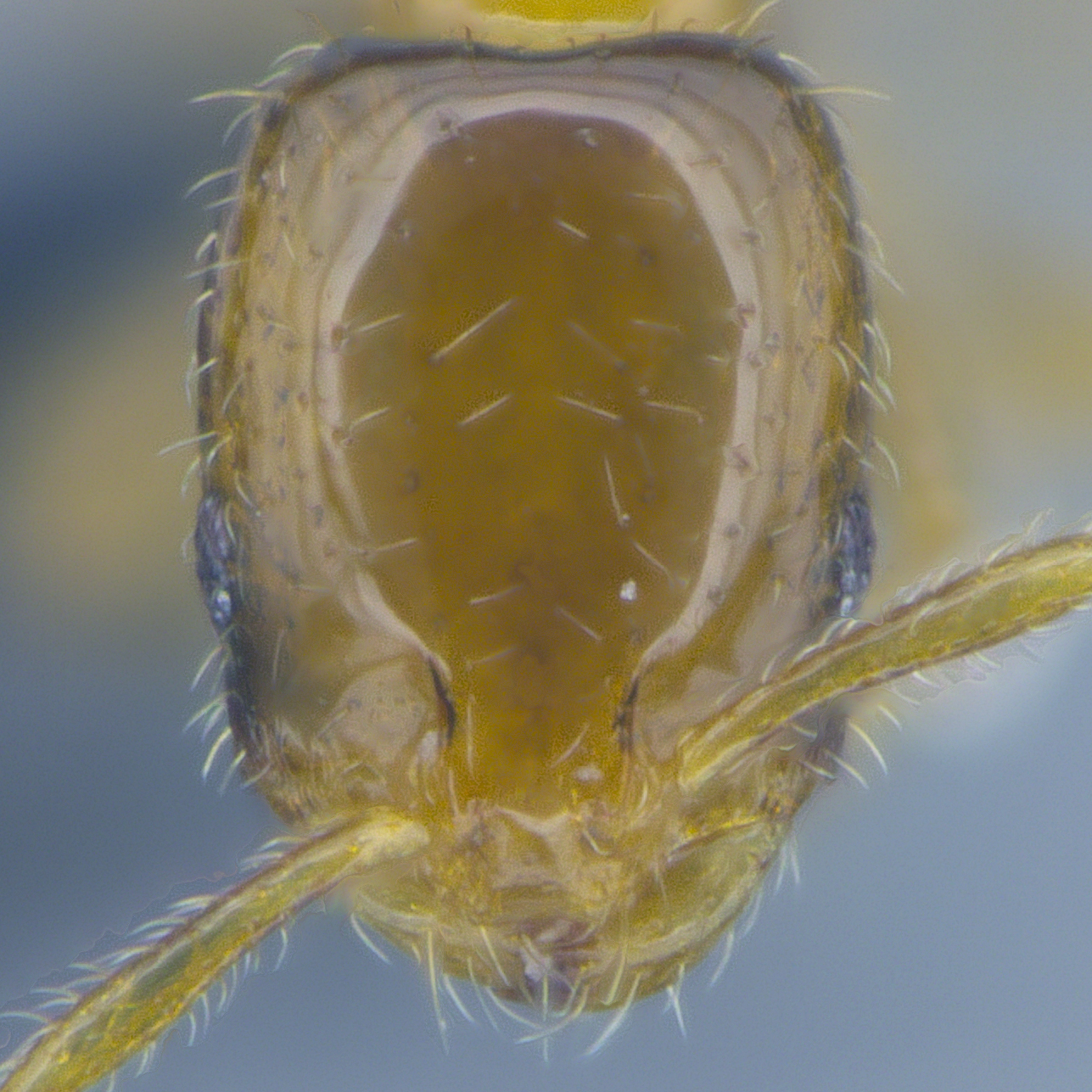
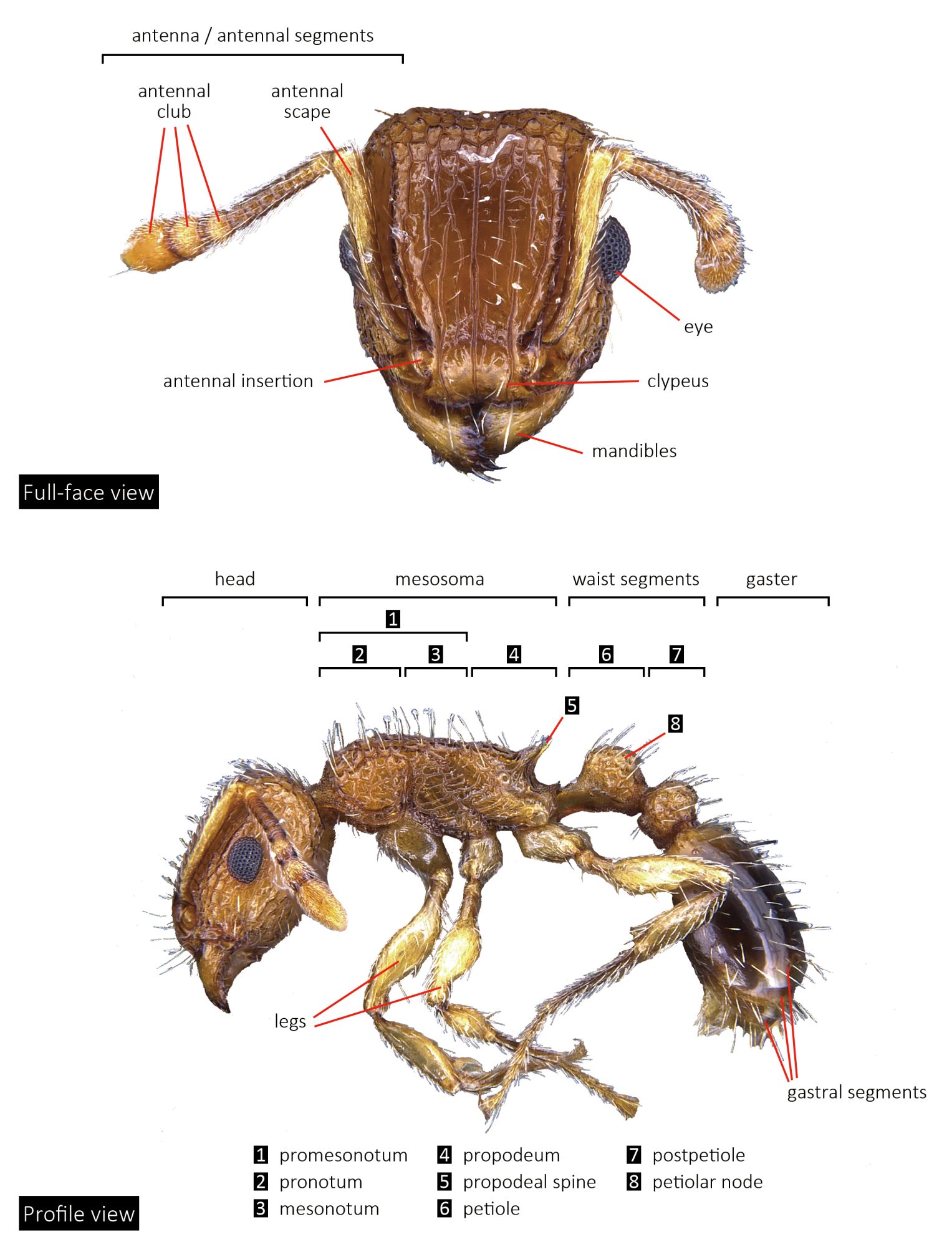
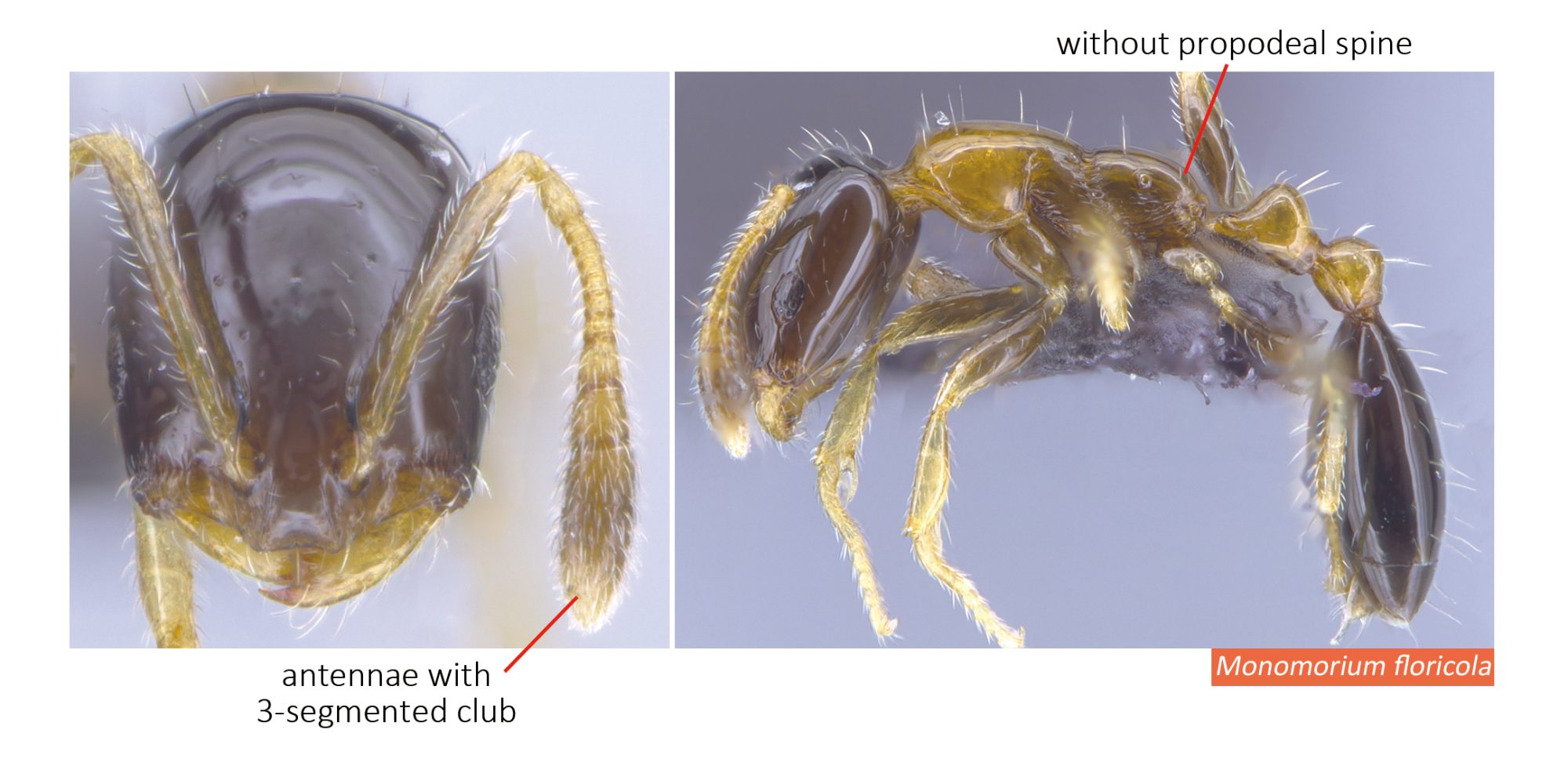
Monomorium species are very small to medium in size (1–4 mm), mostly with yellow, red or brown coloration, but there are also species that have darker coloration. They can be recognized by their 12- or 11-segmented (rarely 10-segmented) antennae with 3-segmented club, the lack of spine on the back, and the shape of petiole.

Species in this genus