Subfamily PONERINAE
GENUS
Pseudoneoponera
Donisthorpe, 1943
Foamy ants
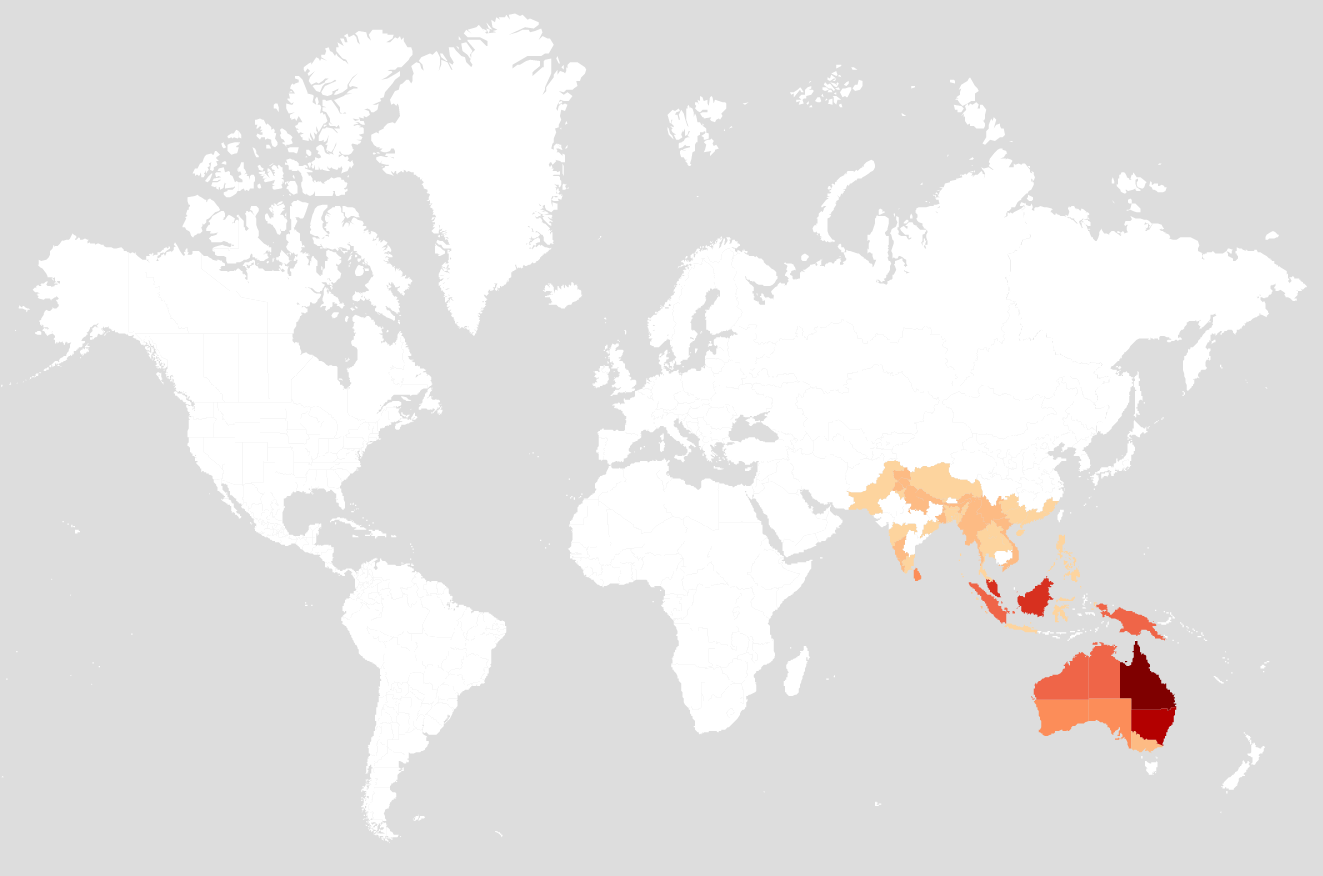
Distribution.
A small ant genus with 19 species described. The genus has a limited distribution, restricted to tropical and subtropical regions of East Asia and Oceania, with the diversity being highest in Australia.
Biology & Ecology.
Nests of Pseudoneoponera species are usually located within the soil, but sometimes on trees. Nests are very small and contain only one to two dozen of workers, and usually forming polygynous colonies (more than one egg-laying female per colony).
Pseudoneoponera species are solitary predatory ants feeding on arthropods. Workers’ foraging activity is limited to within leaf litter (and on trees for arboreal species) of forest habitats.
Workers are known to produce foam-like secretion from the venom glands for defense, such as against other ants. The foam is used to physically immobilize the opponents.
Pseudoneoponera species use an uncommon reproductive strategy: apart from queens, some workers (known as gamergates) are also responsible for mating and reproduction. In some species of the genus, queen caste is even completely absent. All the reproductive and mated individuals (queens and gamergates) compete for egg-laying role.
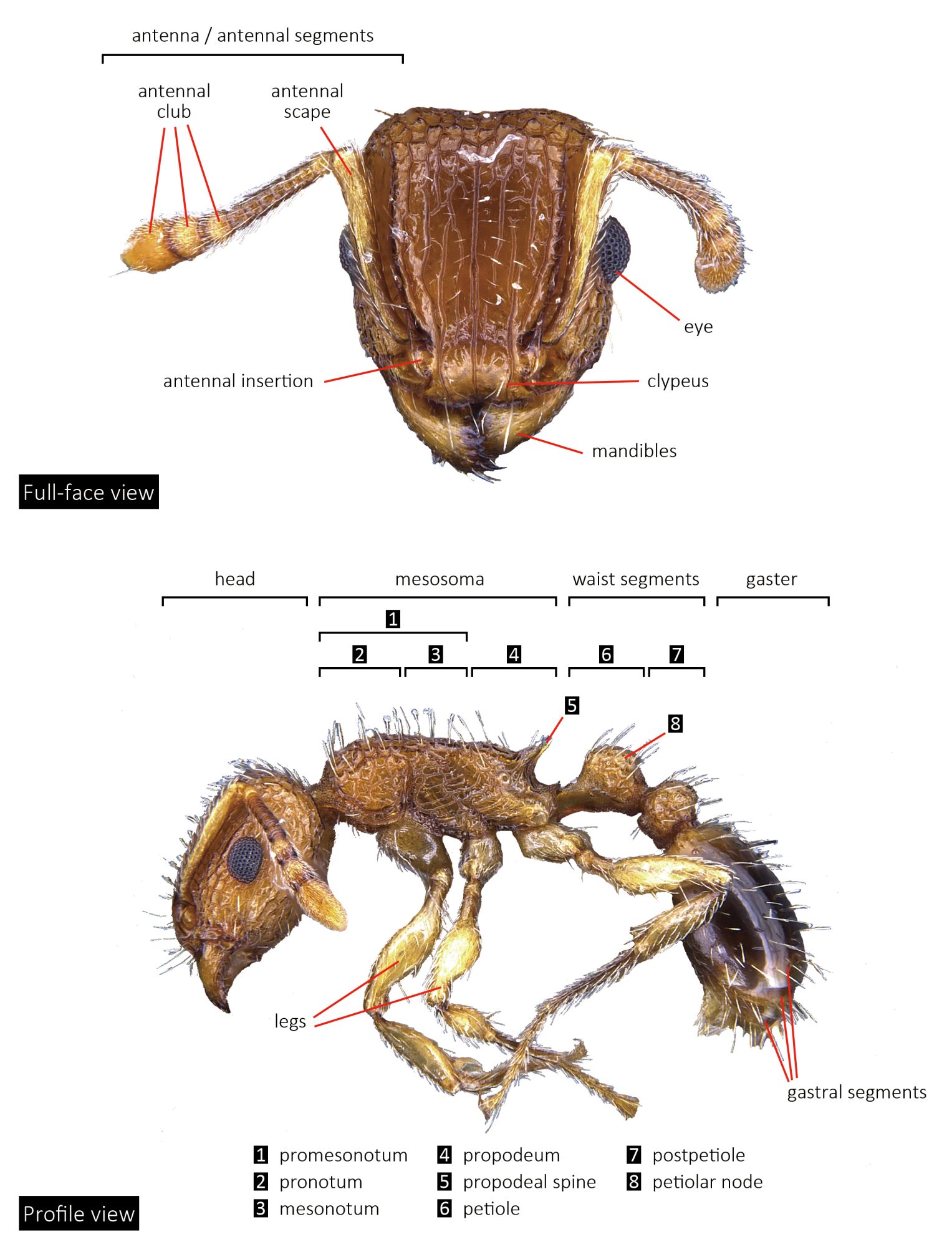
Identification.
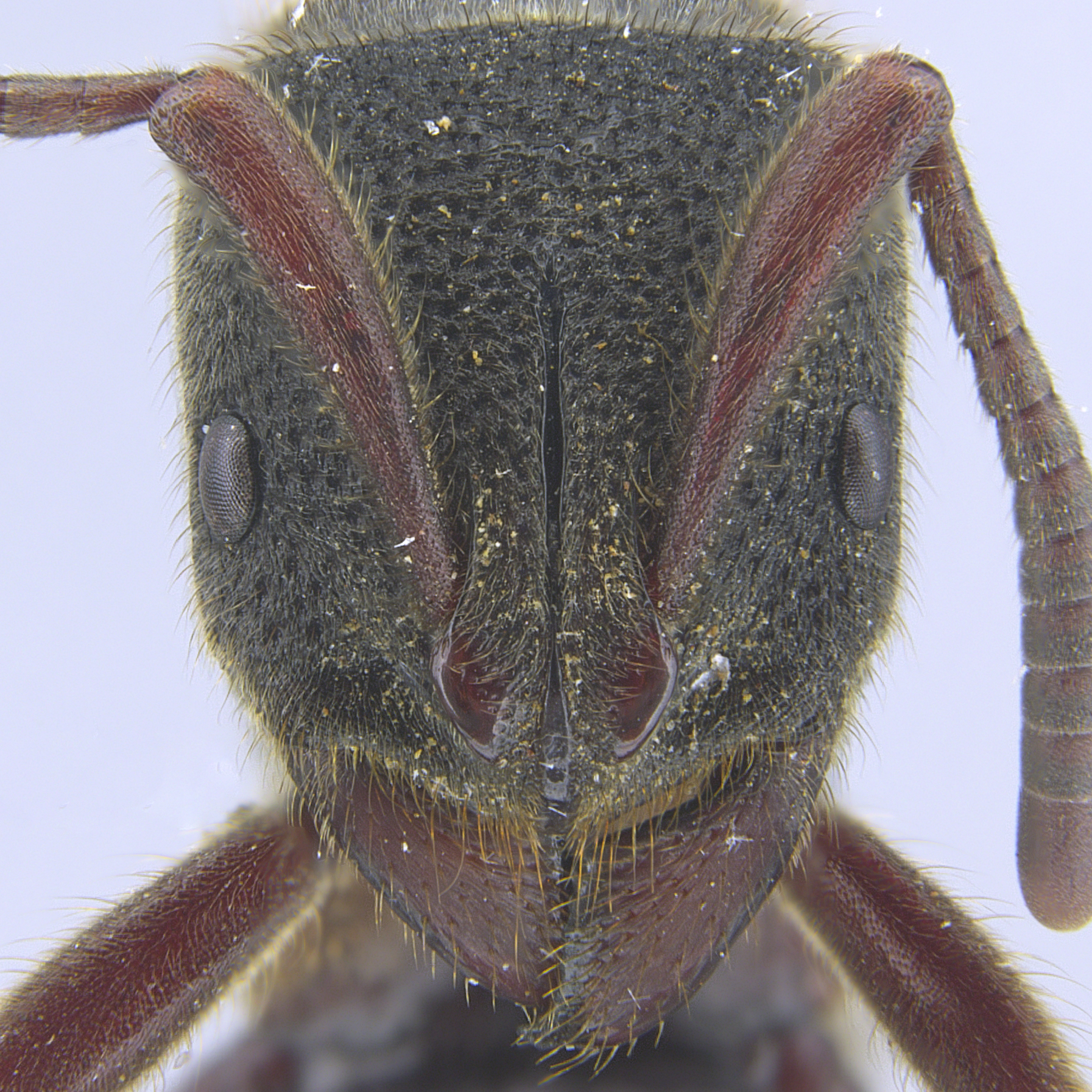
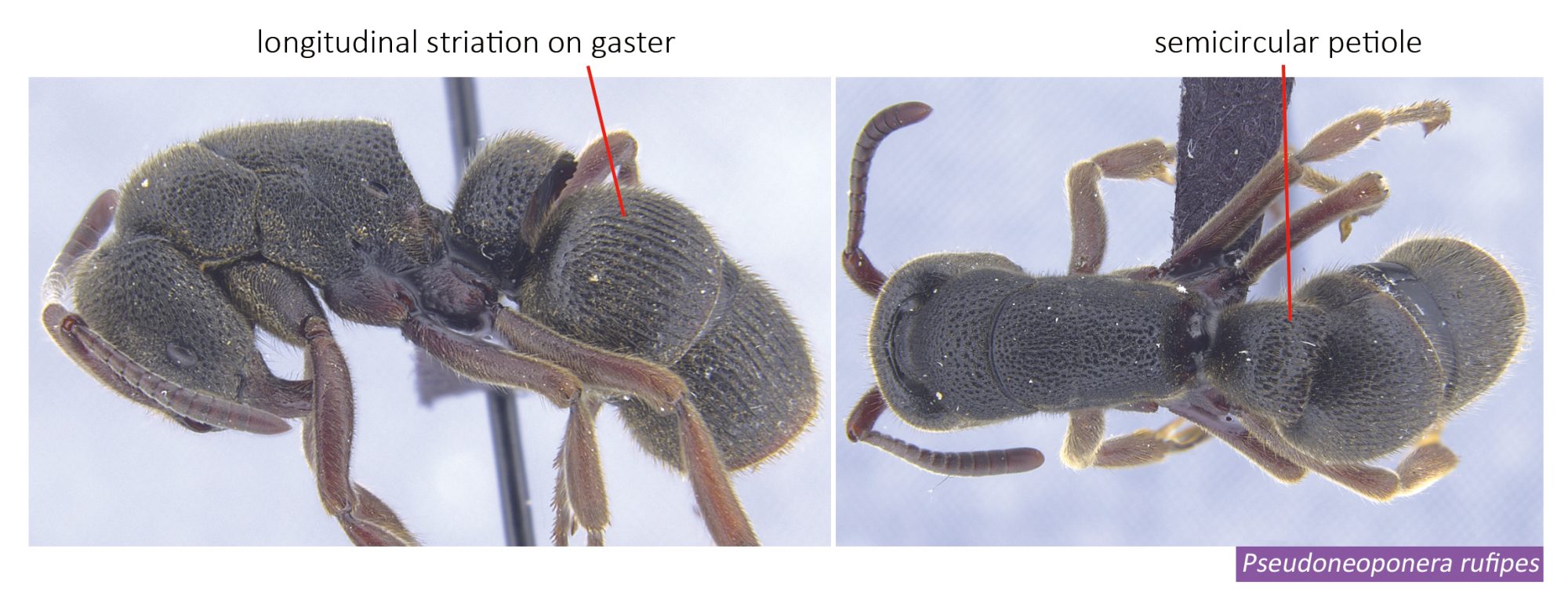
Pseudoneoponera species are very large in size (11–16 mm), with reddish brown to black coloration. They can be easily recognized by their size and, in dorsal view, the semicircular waist segment with denticles in the posterior margin, and longitudinally-striated gaster.

Species in this genus