Subfamily MYRMICINAE
GENUS
Solenopsis
Westwood, 1840
Thief ants / Fire ants
Distribution.
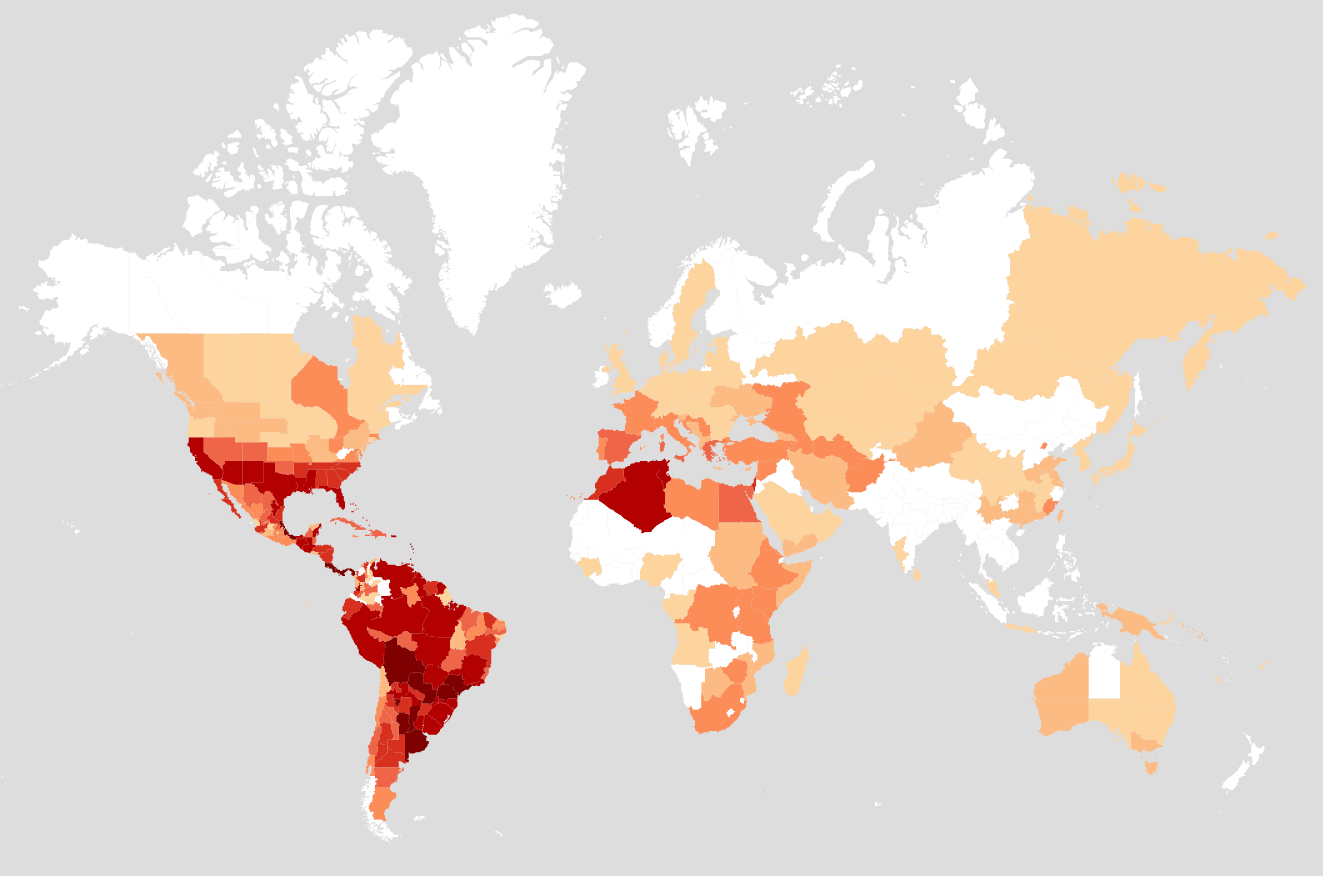
A large ant genus with 191 species described. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution and can be found on all continents, with the diversity being highest in the New World.
Biology & Ecology.
Solenopsis species have highly diverse lifestyle, nests are usually located within the soil, and forage above the ground or within leaf litter. Nests are small to large, contain a dozen of workers to hundreds of thousands of workers.
Most of the species are small, monomorphic subterranean ants, also known as thief ants, for they nest close-to or inside colonies of other ants or termites and steal food or brood from them.
A further 5 species are social parasites, which have no worker caste and use the host colony of other species of ants to raise their brood.
Some of the New World species have larger, polymorphic workers and have much bigger colonies. These species are aggressive above-the-ground foragers and are known for characteristic sting that comes with intense burning sensation, hence their common name fire ants. Many of the fire ants are pest and invasive species with worldwide distribution, including the infamous red imported fire ants (S. invicta).
Identification.
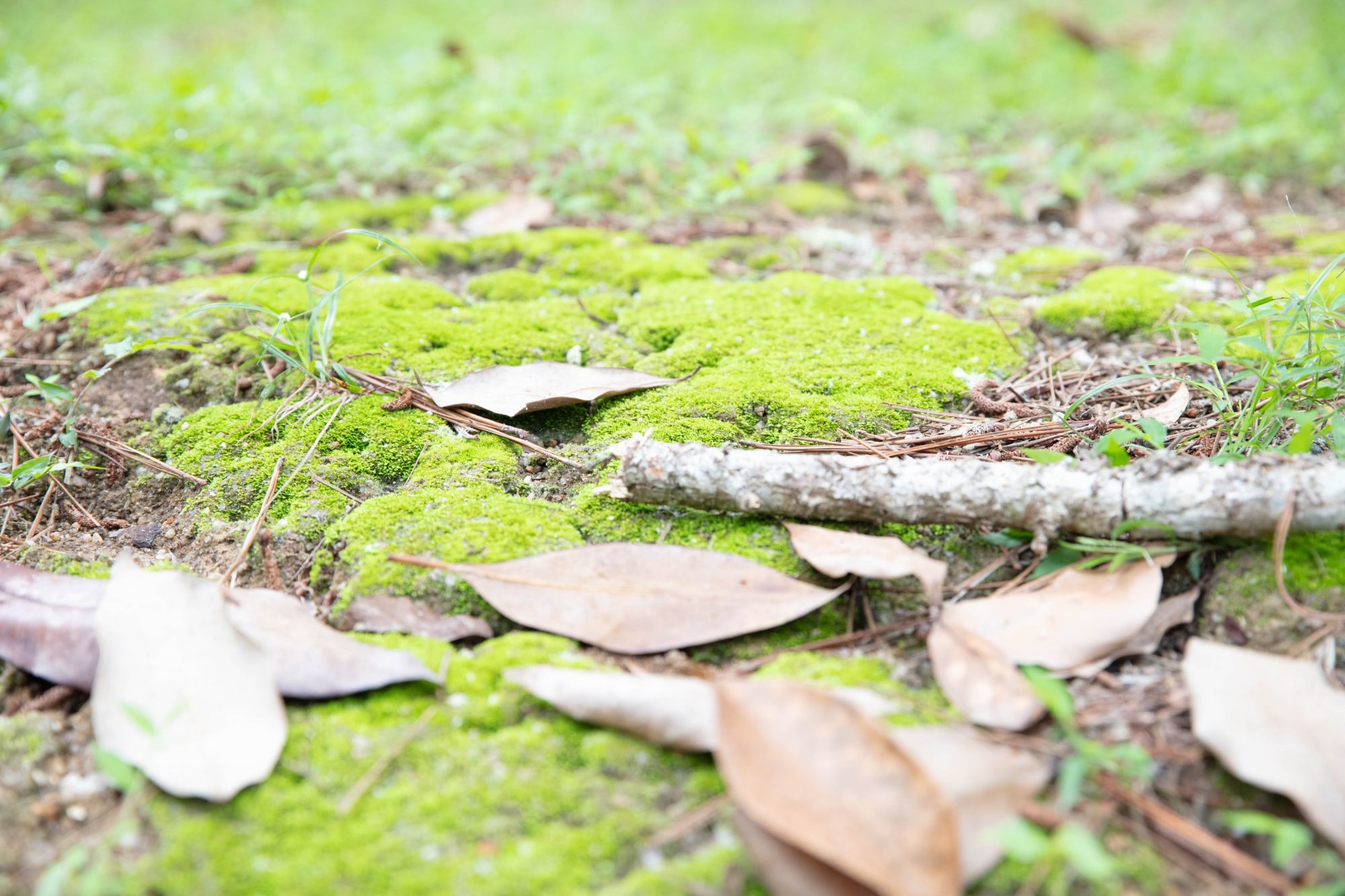
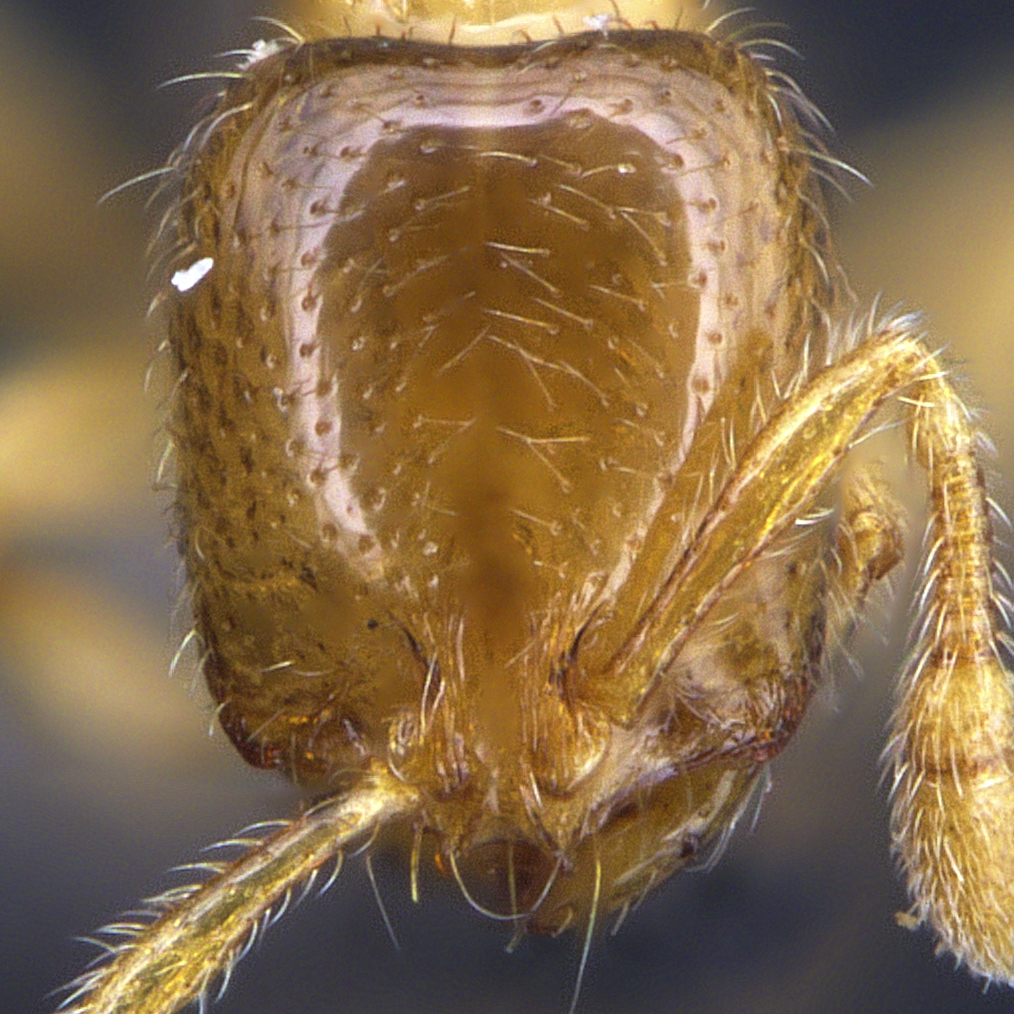
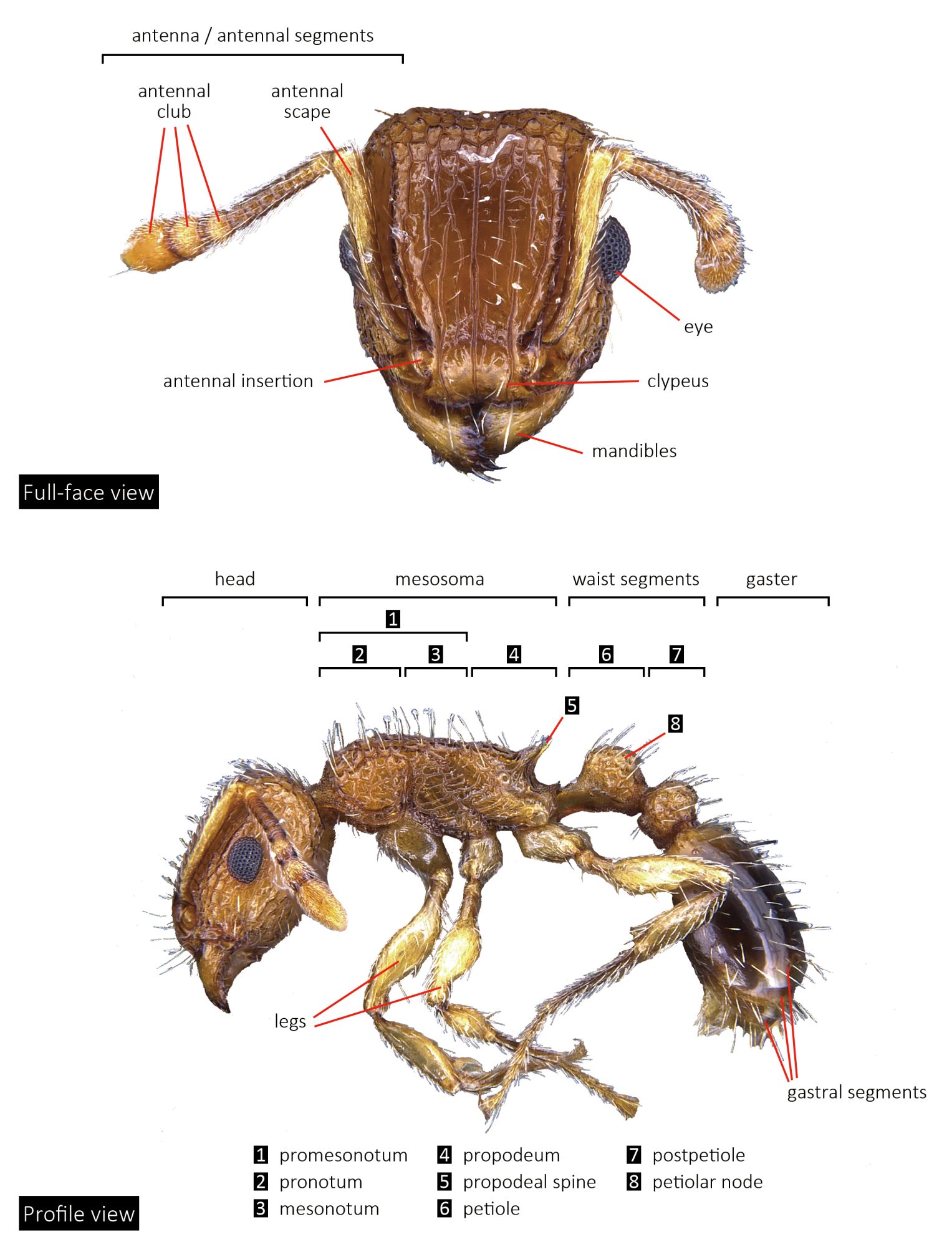
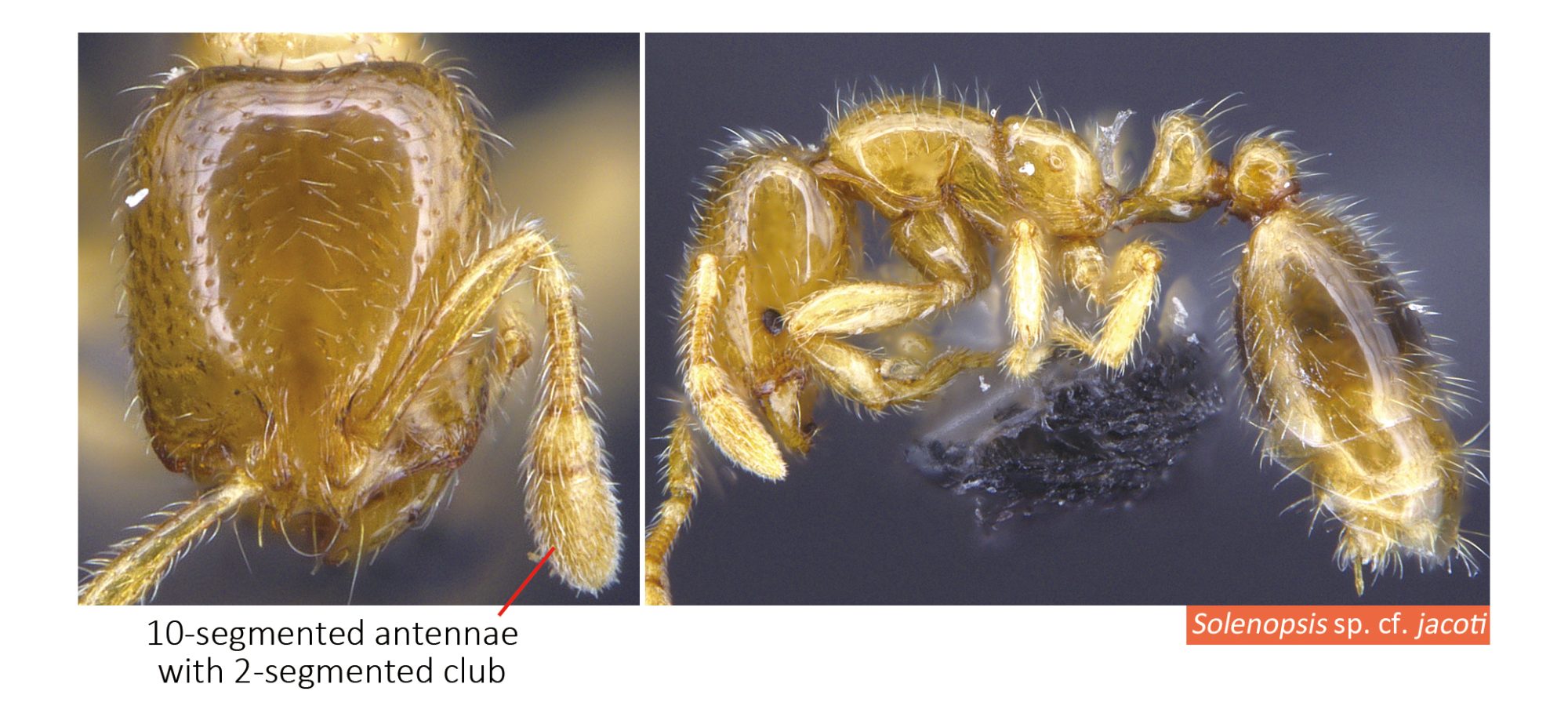
Solenopsis species are very small to medium in size (1–7 mm), mostly with yellow to brown coloration, while fire ants are often red in color. They can be recognized by their 10-segmented antennae with 2-segmented club.

Species in this genus