Subfamily MYRMICINAE
GENUS
Tetramorium
Mayr, 1855
Pavement ants
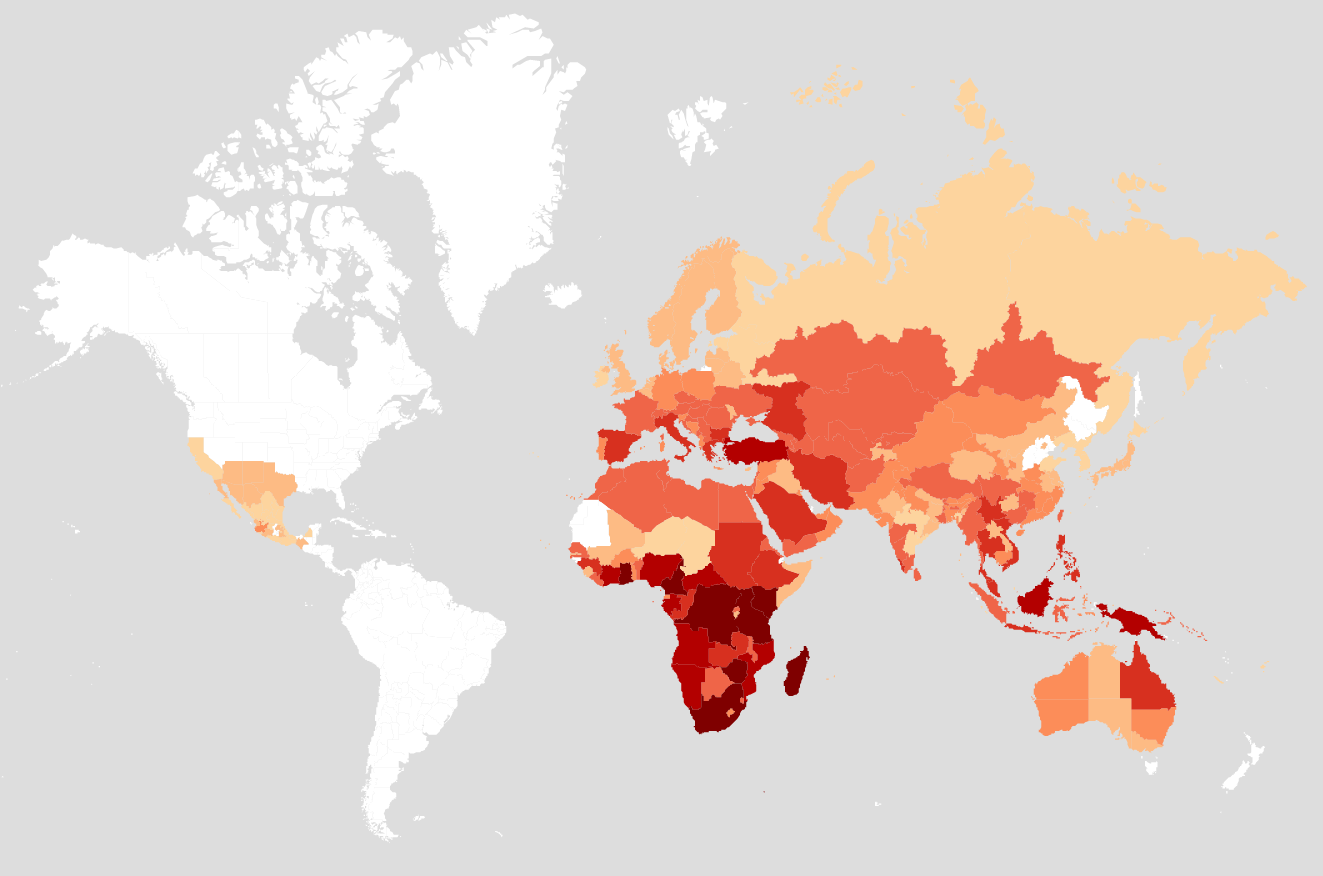
Distribution.
A very successful ant genus with 588 species described. The genus has a very widespread distribution in the Old World, with the diversity being highest in Africa. A few species might have established in North America as early as the 18th century.
Biology & Ecology.
Tetramorium species have highly diverse lifestyle, nests are usually located within the soil and decaying wood, but some species are considered arboreal. Nests are large and contain up to tens of thousands of workers.
Tetramorium species are mostly hunter, while some species from the African savannah are granivores (seed-eaters). Workers’ foraging activity, depending on the species’ lifestyle, is either above the ground or on trees.
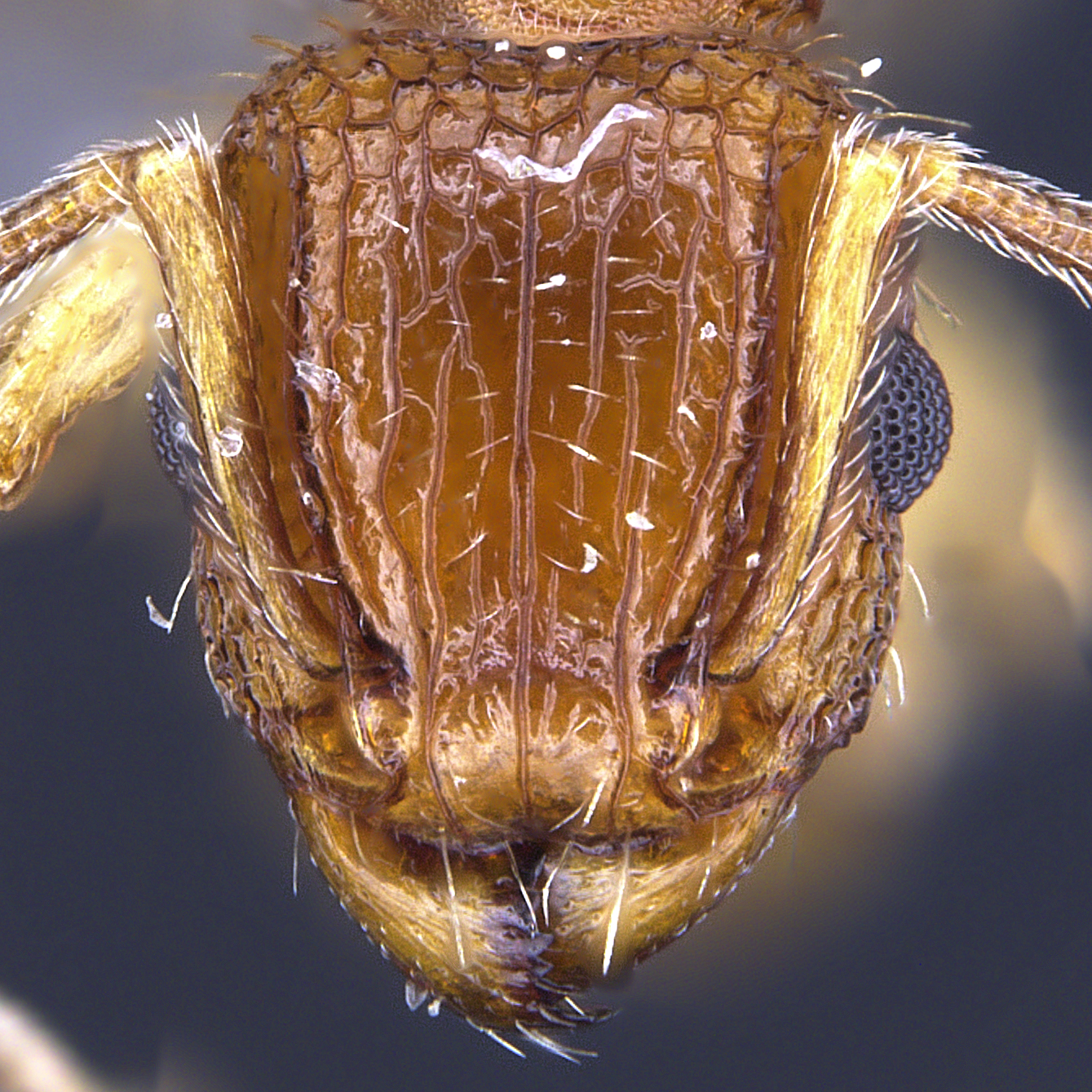
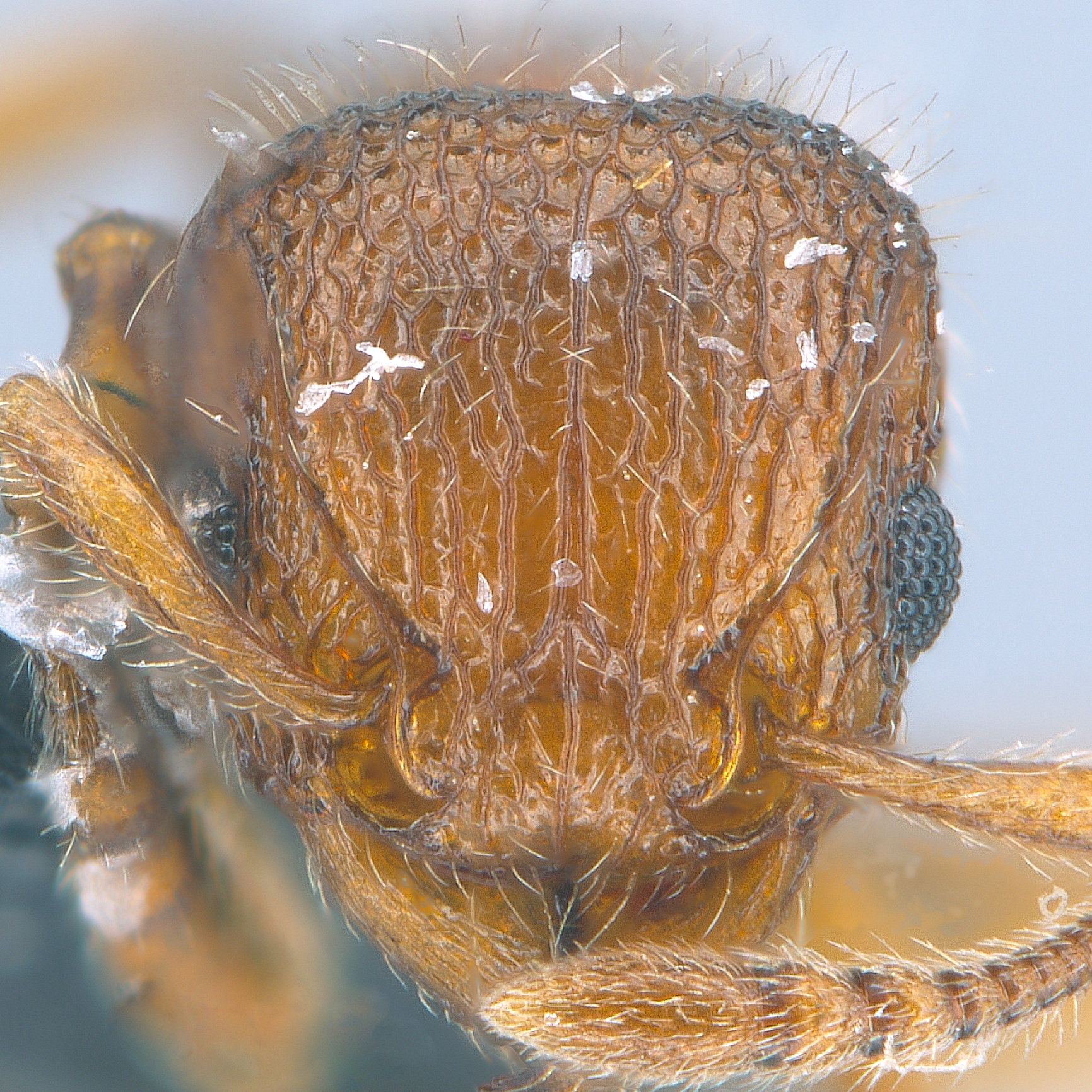
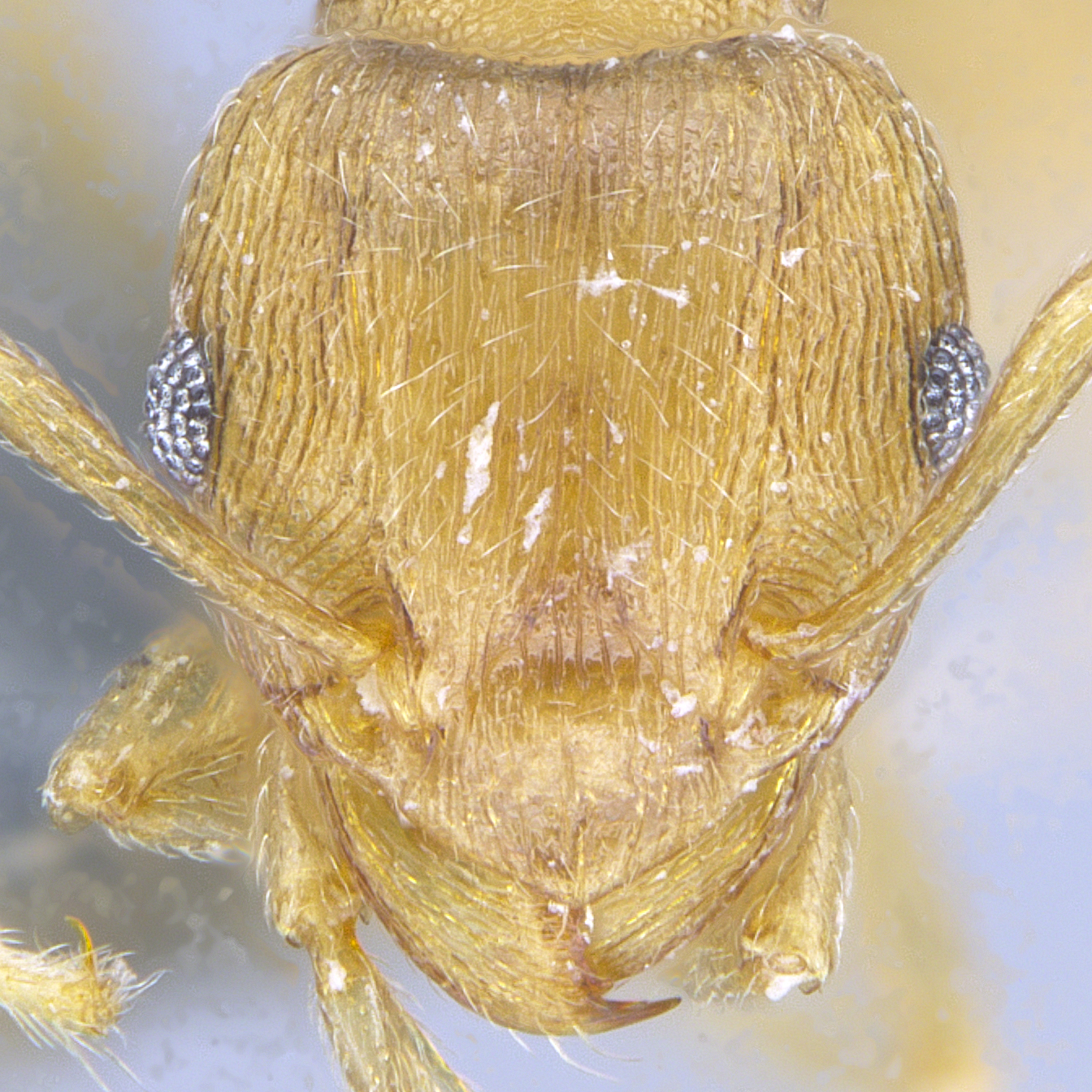
Identification.
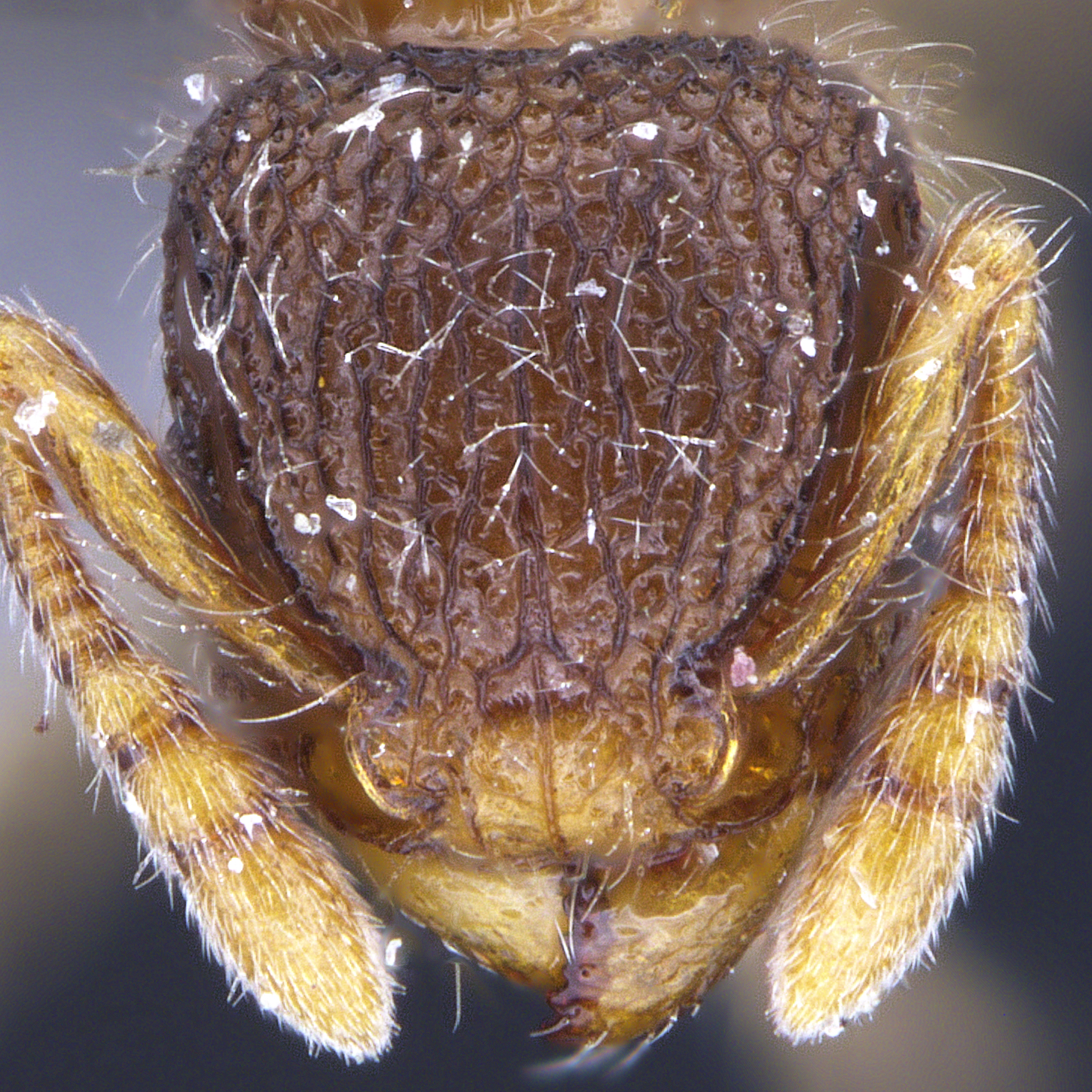
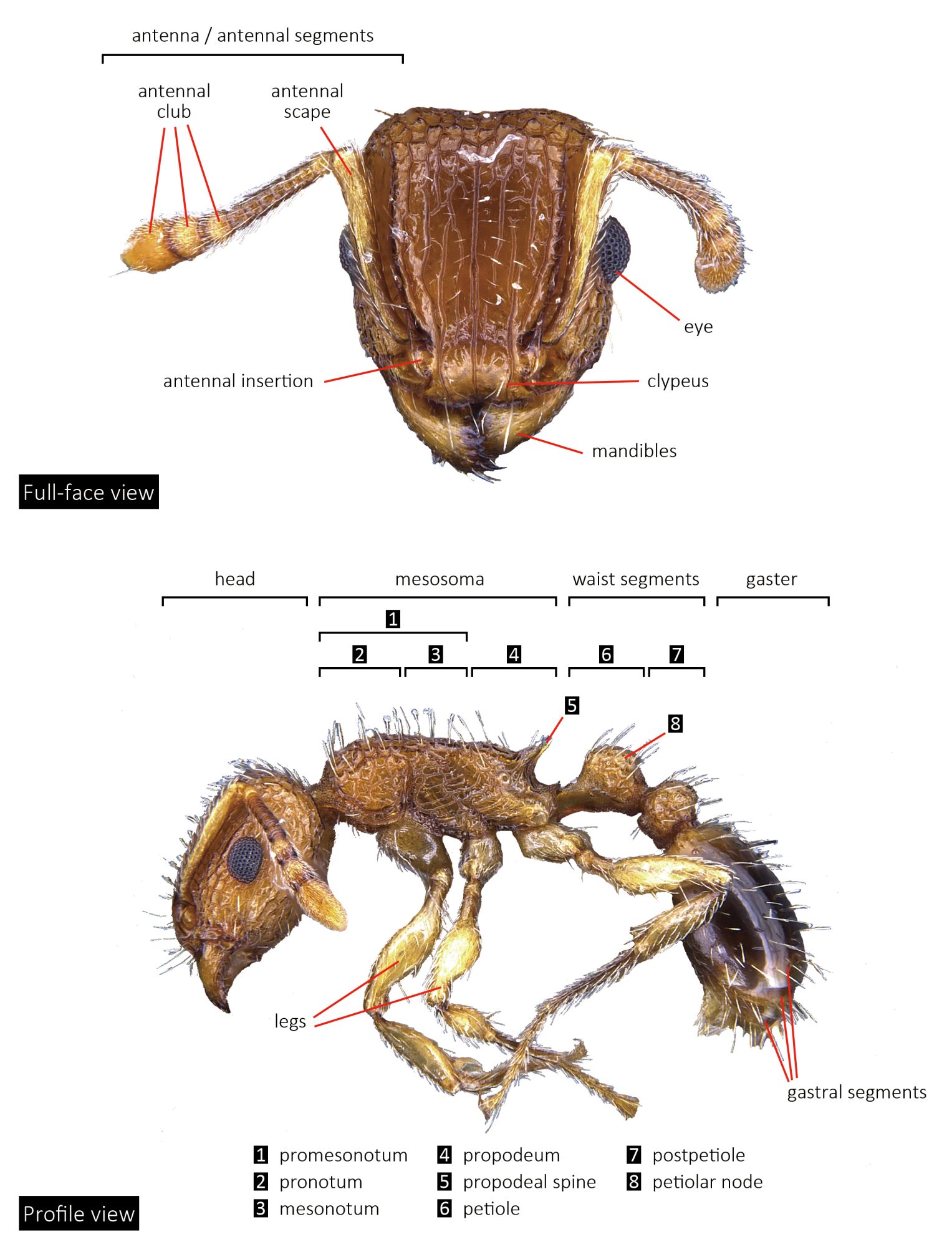
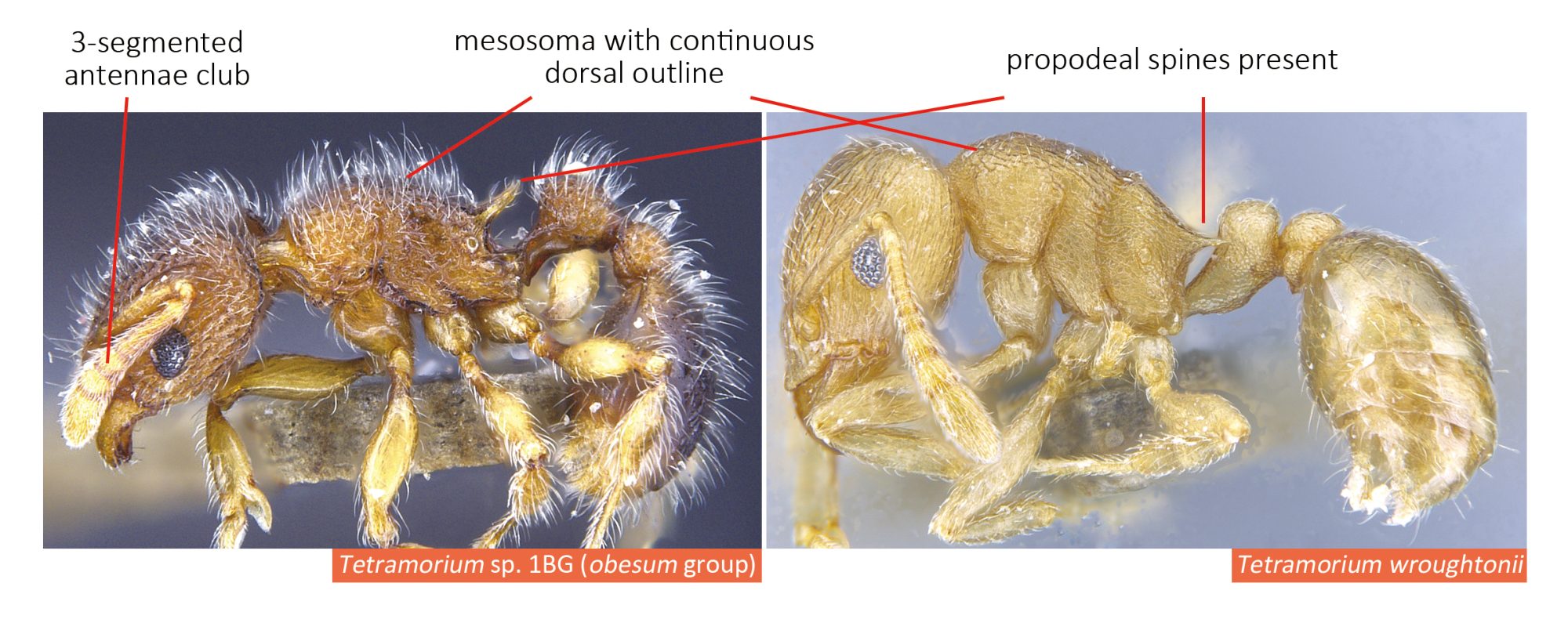
Tetramorium species are medium in size (3–5 mm), mostly with brown, dark brown and black coloration, but there are also species that have lighter coloration. They can be recognized by their 12-segmented antennae (sometimes 11- or 10-segmented) with 3-segmented club, large eyes, mesosoma with a continuous contour (often relatively flat), and the presence of spines on the posterior portion of their mesosoma (propodeum).

Species in this genus